Day 15: Mastering Python Fundamentals
Nov 12, 2024
•11:20 PM GMT+8

The objective of this post is to cover the essentials of Python programming, including quotes, comments, variables, print formatting, and data structures. As we learn more about Python, these basic concepts will help us to understand more complex concepts in the future.
Quotes and Comments
Comments in Python allow developers to write notes or explanations in their code, which are ignored during execution. Python also uses quotes for string literals.
- Single-line Comments
Use#for single-line comments, which help in documenting code.
# This is a single-line comment
print("Hello DevOps Engineer!")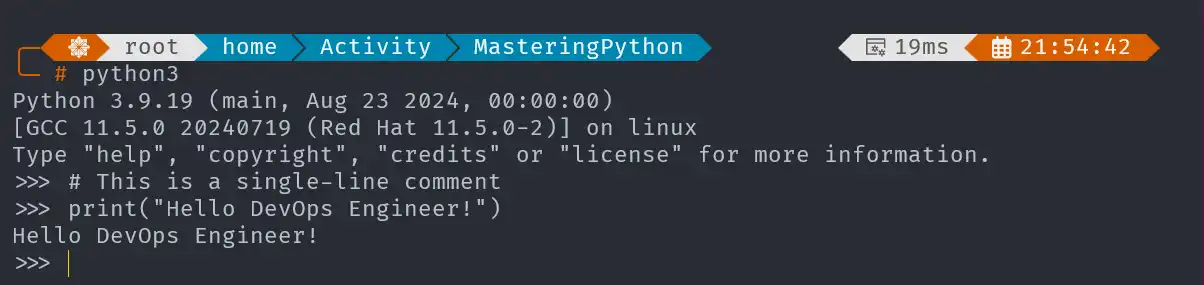
- Multi-line Comments
Use triple quotes for multi-line comments, ideal for longer descriptions or notes.
"""
This is a multi-line comment.
It spans multiple lines.
"""
print("Hello DevOps Engineer!")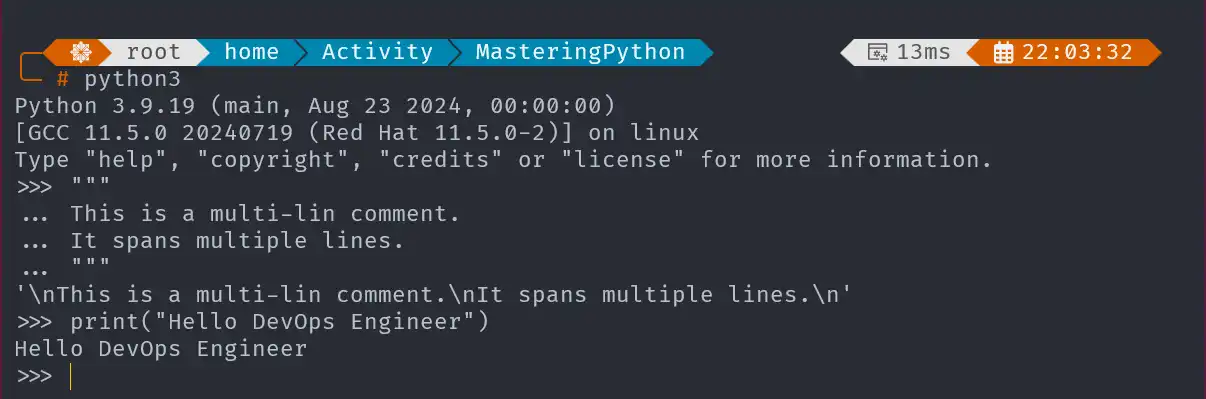
Variables
Variables in Python are used to store data values, and they can be created by assigning a value to a name. In addition to following best practices, variable names should also be descriptive (e.g., lowercase with underscores).
- Rules for Naming Variables
- Use letters, numbers, and underscores.
- Variable names cannot start with a number.
- Avoid Python keywords (e.g.,
print,for,if).
- Example of Variable Assignments
name = "Adrian"
id = 1
is_devops_engineer = TruePrint Format
Printing output in Python can be done in multiple ways, with f-strings and .format() being among the most popular methods for formatting strings.
- f-Strings Method
Embed variables directly within strings. .format()Method
Use the.formatmethod for formatting strings.
# f-Strings Method
print(f"Hello, {name}!\n")
# .format Method
print("The id number is {} and the is_devops_engineer value is {}.".format(id,is_devops_engineer))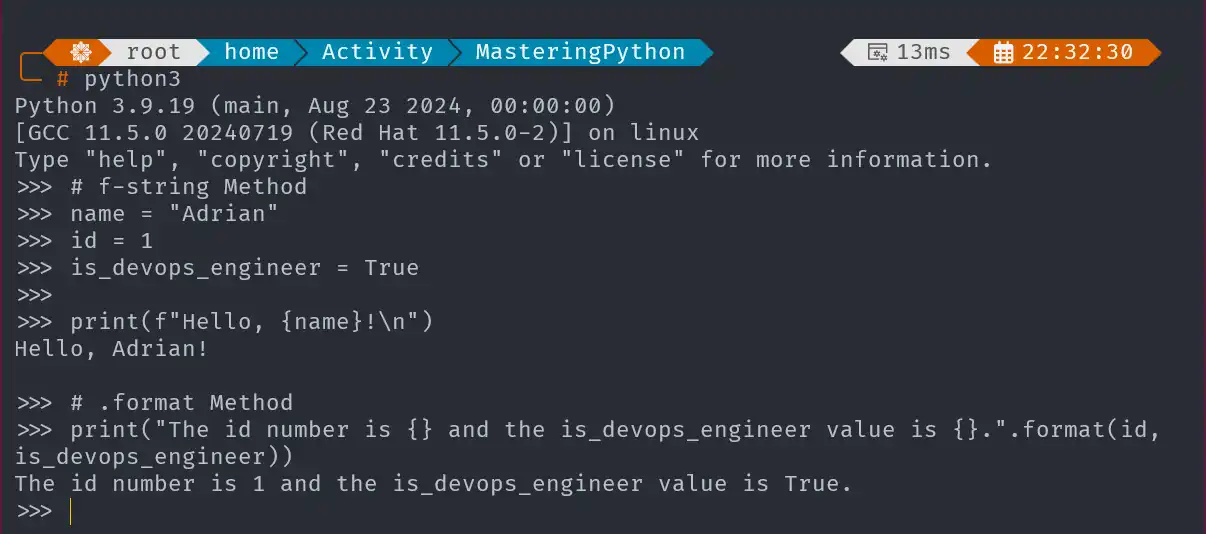
Data Structures
The data structures in Python are extremely helpful when it comes to organizing, managing, and storing data efficiently. Various data structure types provide different techniques for handling data, from simple numbers to complex collections, enabling developers to choose the right structure for specific tasks. It is fundamental to master these structures in Python so that your code will be cleaner, more efficient, and easier to read.
| Data Type | Description | Example |
| Integer | Whole numbers, positive or negative | id = 01 |
| Float | Numbers with decimals | pi = 3.14 |
| String | Text data, enclosed in quotes | language = "Python" |
| Boolean | Represents True or False values | is_active = True |
| List | Ordered, mutable collection | tech_stack = ["linux", "python", "docker"] |
| Tuple | Ordered, immutable collection | coordinates = (10, 20) |
| Dictionary | Key-value pairs, mutable | tech_dict = { 1: "Linux", 2: "Docker", 3: "Ansible" } |
| Set | Unordered, mutable collection of unique items | cloud_providers = {"aws", "azure", "gcp"} |
Tasks
Differences Between List, Tuple, and Set
Compare the properties of these data structures to understand their unique characteristics.
# List
tech_stack = ["linux", "python", "docker"]
tech_stack.append("oracle")
# Tuple
coordinates = (10, 20)
# Set
cloud_providers = {"aws", "azure", "gcp"}
cloud_providers.add("oracle")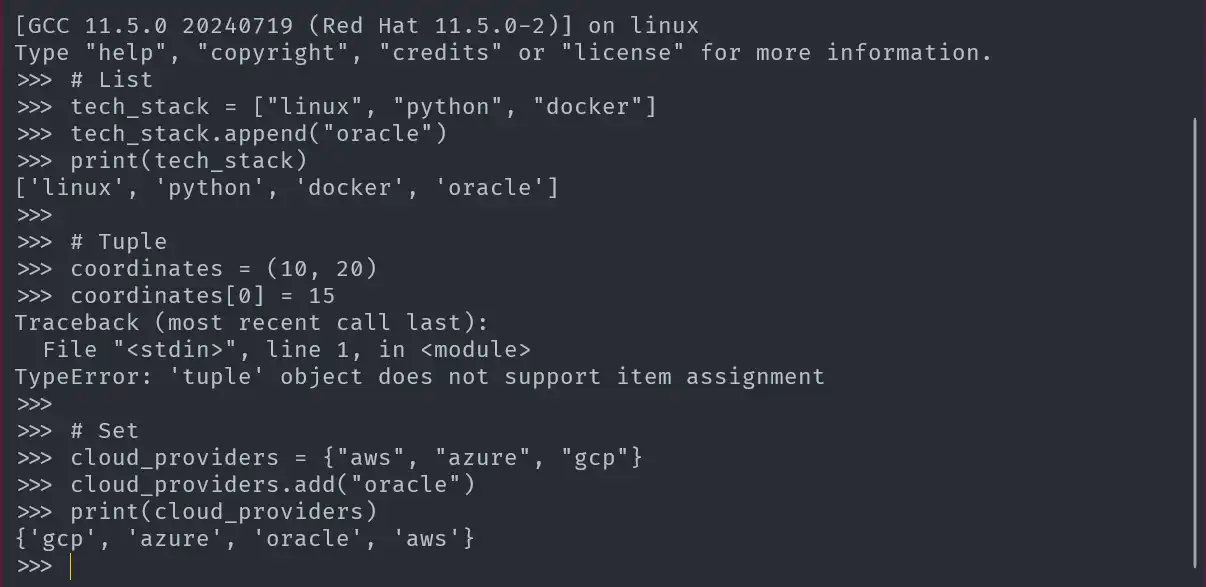
Comparison Table
| Property | List | Tuple | Set |
| Syntax | [ ] | ( ) | { } |
| Mutable | Yes | No | Yes |
| Ordered | Yes | Yes | No |
| Duplicates Allowed | Yes | Yes | No |
Create a Dictionary and Print Values by Key
In this task, we will create a dictionary and access its values using keys. Each key to directly retrieve and print the associated value. This method is efficient for quickly accessing specific items in the dictionary. Here is an example below:
# Creating the dictionary
tech_dict = { 1: "Linux", 2: "Docker", 3: "Ansible" }
tech_dict_key = 3
print(f"The {tech_dict[tech_dict_key]} is one of essential in DevOps skills.")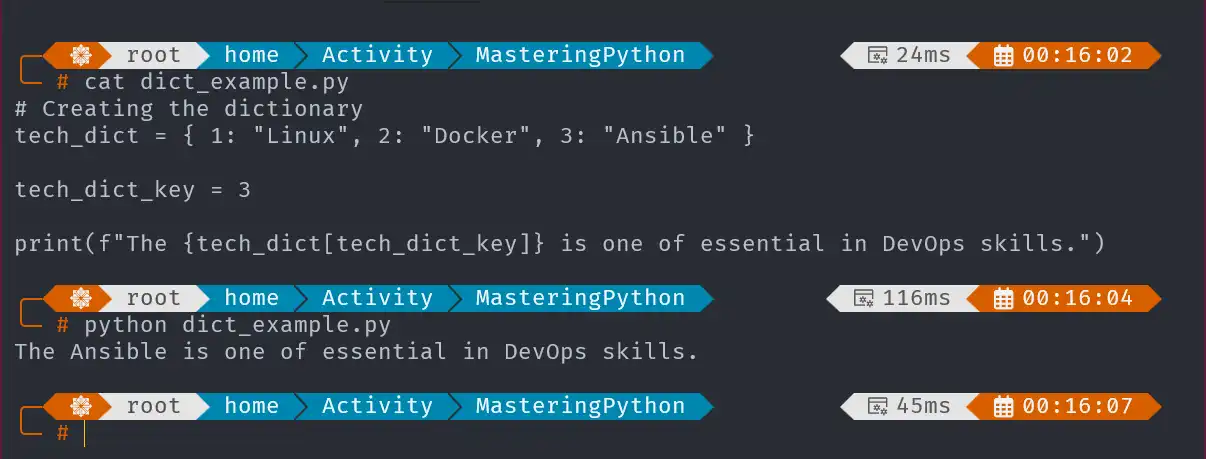
Create a List of Azure Services
Create a list of Azure services and use some list methods to manage the data.
# List of Azure Services
azure_services = ["Virtual Machines", "Function Apps", "Logic Apps"]
# Add Item
azure_services.append("Cosmos DB")
# Sorts in-place
azure_services.sort()
# Reverses the elements of the list in-place
azure_services.reverse()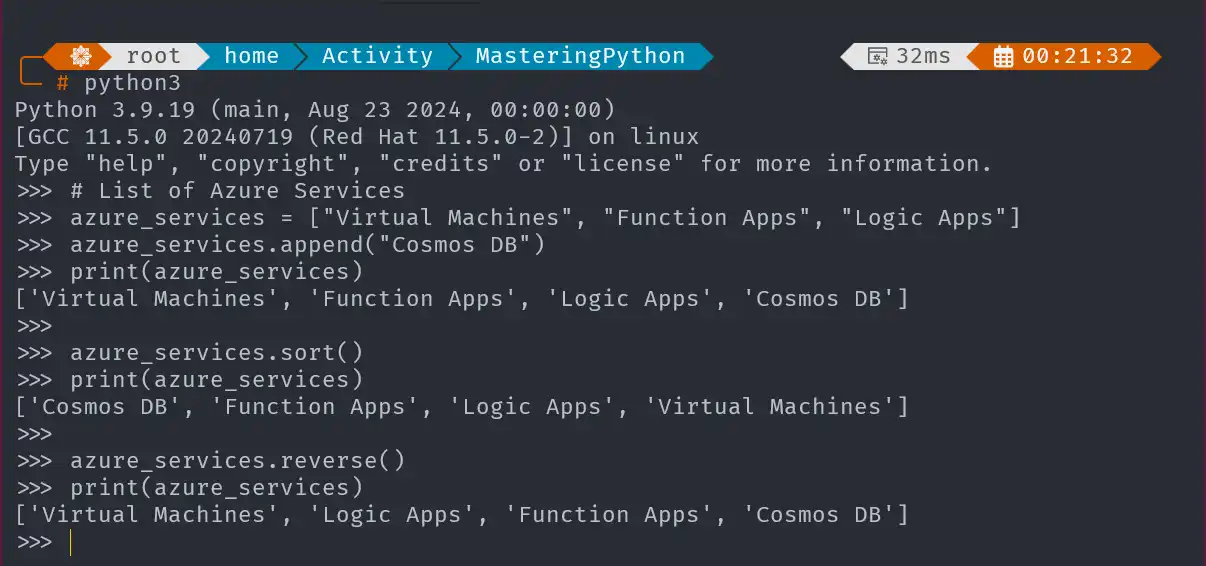
Conclusion
In this post, we discussed Python fundamentals such as variables, print formatting, and data structures. A solid understanding of these basic concepts is a must for anyone who intends to master Python for DevOps or other applications. Our next blog will explore Python's control flow, operators, and core structures.
Day 15: Mastering Python Fundamentals
Learn the essentials of Python, including comments, variables, print formatting, and core data structures.
For the passion of automated cloud solutions.
Subscribe to get the latest posts. I mostly write about Backend (Python/Bash), DevOps and Linux.