Day 16: Mastering Python Control Flow and Core Structures
Nov 21, 2024
•11:53 PM GMT+8

The Python control flow and core structures enable developers to write logical, efficient, and reusable code. Throughout this blog, we explore the basics of Python programming, such as operators, conditional statements, and loops.
Operators in Python
It is possible to perform logical operations, computations, and comparisons in Python using various types of operators. The different types of operators play an essential role in control flow and core structures. Here are detailed explanations, examples, and tables for each operator type.
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
x = 10
# Addition
a = x + 5
print(a)
# Subtraction
b = x - 5
print(b)
# Multiplication
c = x * 25
Table of Arithmetic Operators in Python
| Operator | Description | Example |
+ | Addition | x + y |
- | Subtraction | x - y |
* | Multiplication | x * y |
/ | Division | x / y |
% | Modulus | x % y |
** | Exponentiation | x ** y |
// | Floor division | x // y |
Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compare two values and return a Boolean result.
x = 10
# Equal to
print(x == 10)
# Not equal to
print(x != 5)
# Greater than
print(10 > 5)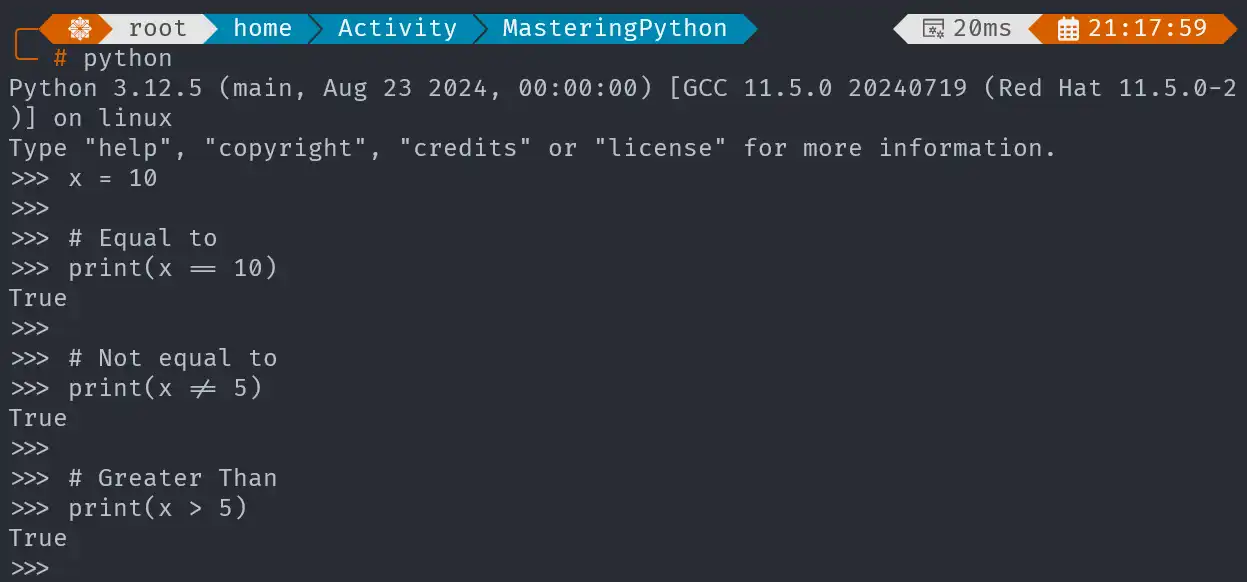
Table of Comparison Operators in Python
| Operator | Description | Example |
== | Equal | x == y |
!= | Not equal | x != y |
> | Greater than | x > y |
< | Less than | x < y |
>= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y |
<= | Less than or equal to | x <= y |
Logical Operators
Logical operators combine multiple conditions and return a Boolean result.
x = 10
# AND operator
print(x > 5 and x < 10)
# OR operator
print(x > 5 or x < 10)
# NOT operator
print(not(x > 5))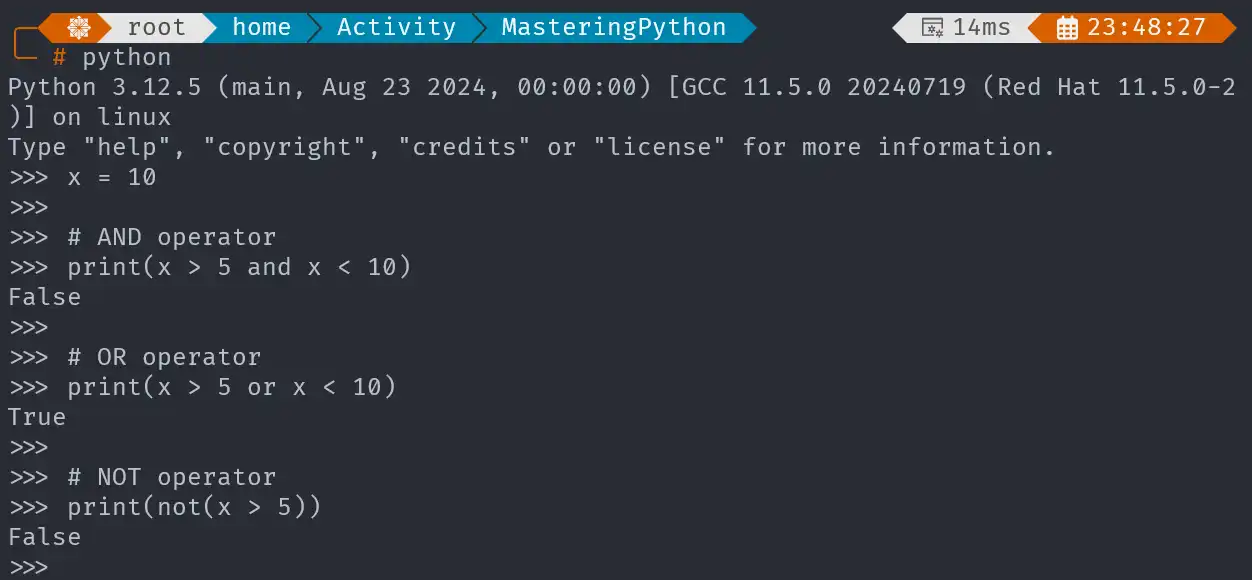
Table of Logical Operators in Python
| Operator | Description | Example |
and | Returns True if both conditions are True | x > 5 and x < 10 |
or | Returns True if at least one condition is True | x > 5 or x < 10 |
not | Reverses the Boolean value | not(x > 5) |
Membership Operators
Membership operators test for membership in a sequence (like a list, tuple, or string).
x = "Azure"
# IN operator
print(x in ["AWS", "GCP", "Azure", "Oracle"])
# NOT IN operator
print("Alibaba" not in ["AWS", "GCP", "Azure", "Oracle"])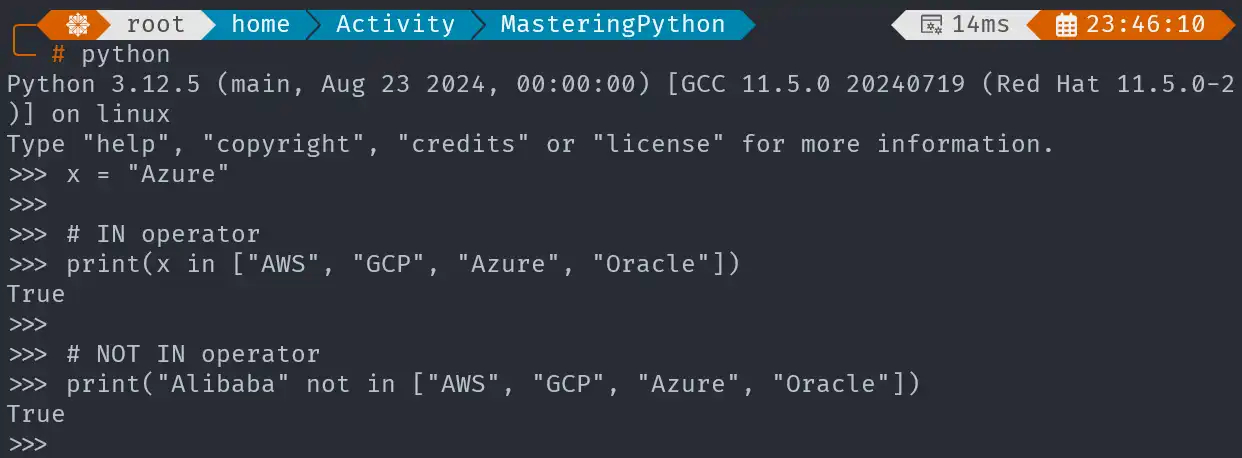
Table of Membership Operators in Python
| Operator | Description | Example |
in | Returns True if value is in sequence. | x in [1, 2, 3] |
not in | Returns True if value is not in sequence. | x not in [1, 2, 3] |
Loops
Loops let you execute code repeatedly until a condition is met. Python supports for and while loops:
- For Loop
Iterates over a sequence (like a list, string, or range).
import time
x = ["Azure", "AWS", "GCP", "Oracle"]
# Iterating through a range
for i in range(3):
print(f"'{x[i]}' is one of the best cloud service providers!")
time.sleep(1)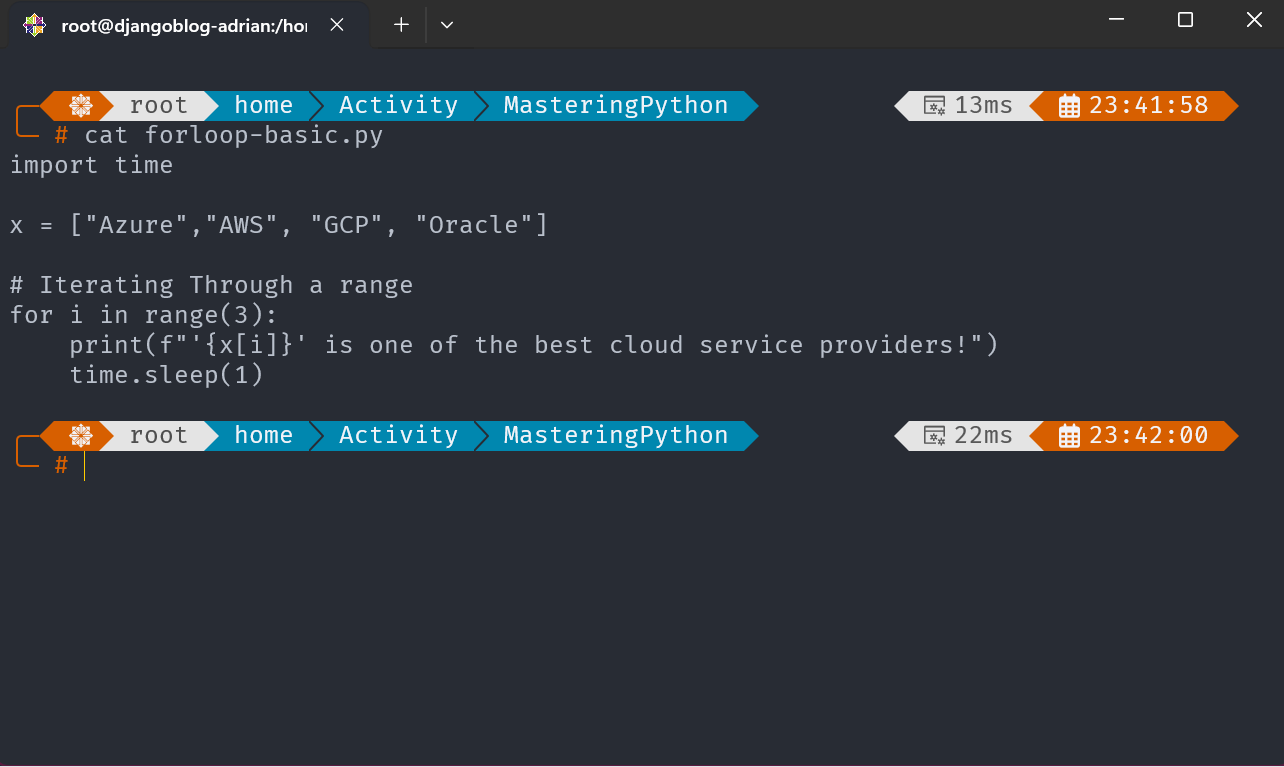
- While Loop
Executes as long as a condition remainsTrue.
import time
x = 5
# Counting down with a while loop
while x > 0:
print(x)
x -= 1
time.sleep(1)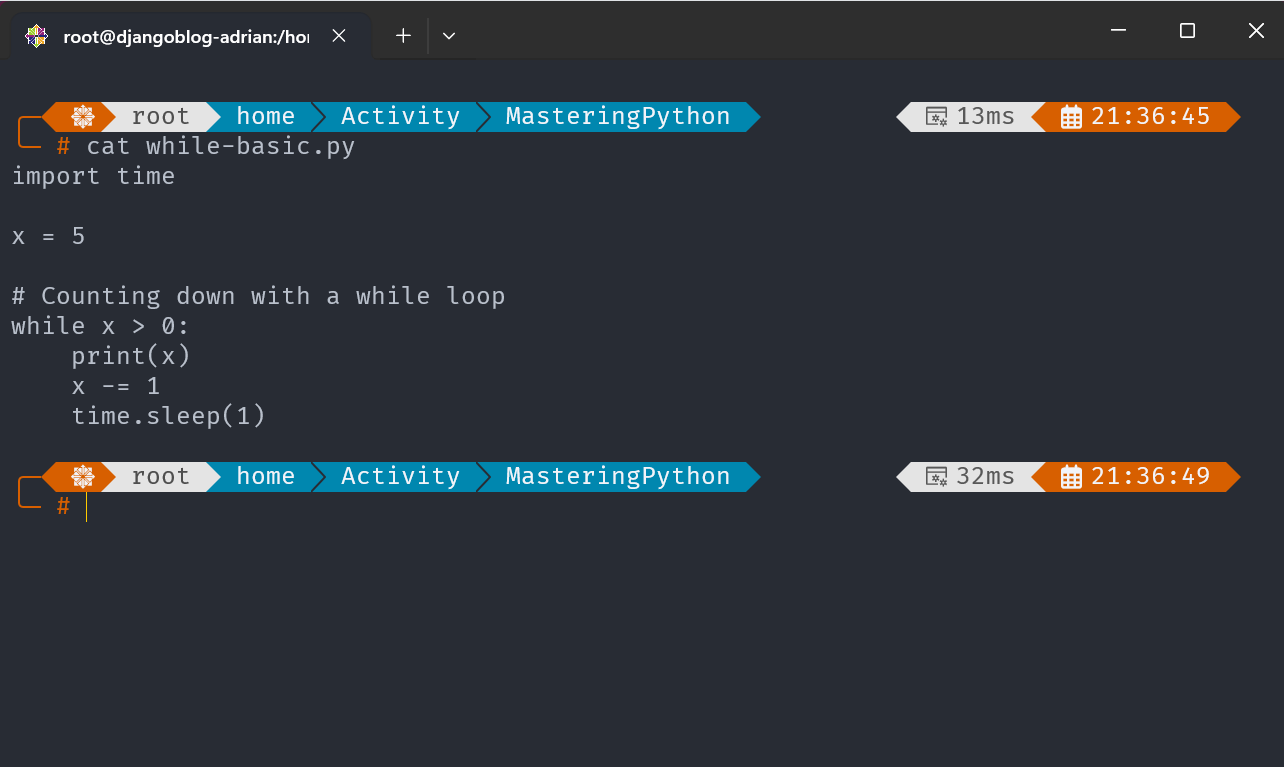
Loop Controls
Loop control statements modify the flow of a loop
| Control | Description | Example |
break | Exits the loop prematurely. | if x == 5: break |
continue | Skips the current iteration and moves to the next. | if x == 5: continue |
pass | A placeholder with no effect on the loop (used for empty blocks). | if x == 5: pass |
import time
x = ["Azure", "AWS", "GCP", "Oracle"]
print("Loop Control - BREAK")
for cloud_provider in x:
if cloud_provider == "GCP":
break # Exit the loop when "GCP" is encountered
print(cloud_provider)
time.sleep(1)
print("")
print("Loop Control - CONTINUE")
for cloud_provider in x:
if cloud_provider == "GCP":
continue # Skip the rest of the iteration for "GCP"
print(cloud_provider)
time.sleep(1)
print("")
print("Loop Control - PASS")
for cloud_provider in x:
if cloud_provider == "GCP":
break
elif cloud_provider == "AWS":
continue
else:
pass # Do nothing for other cloud providers
print(cloud_provider)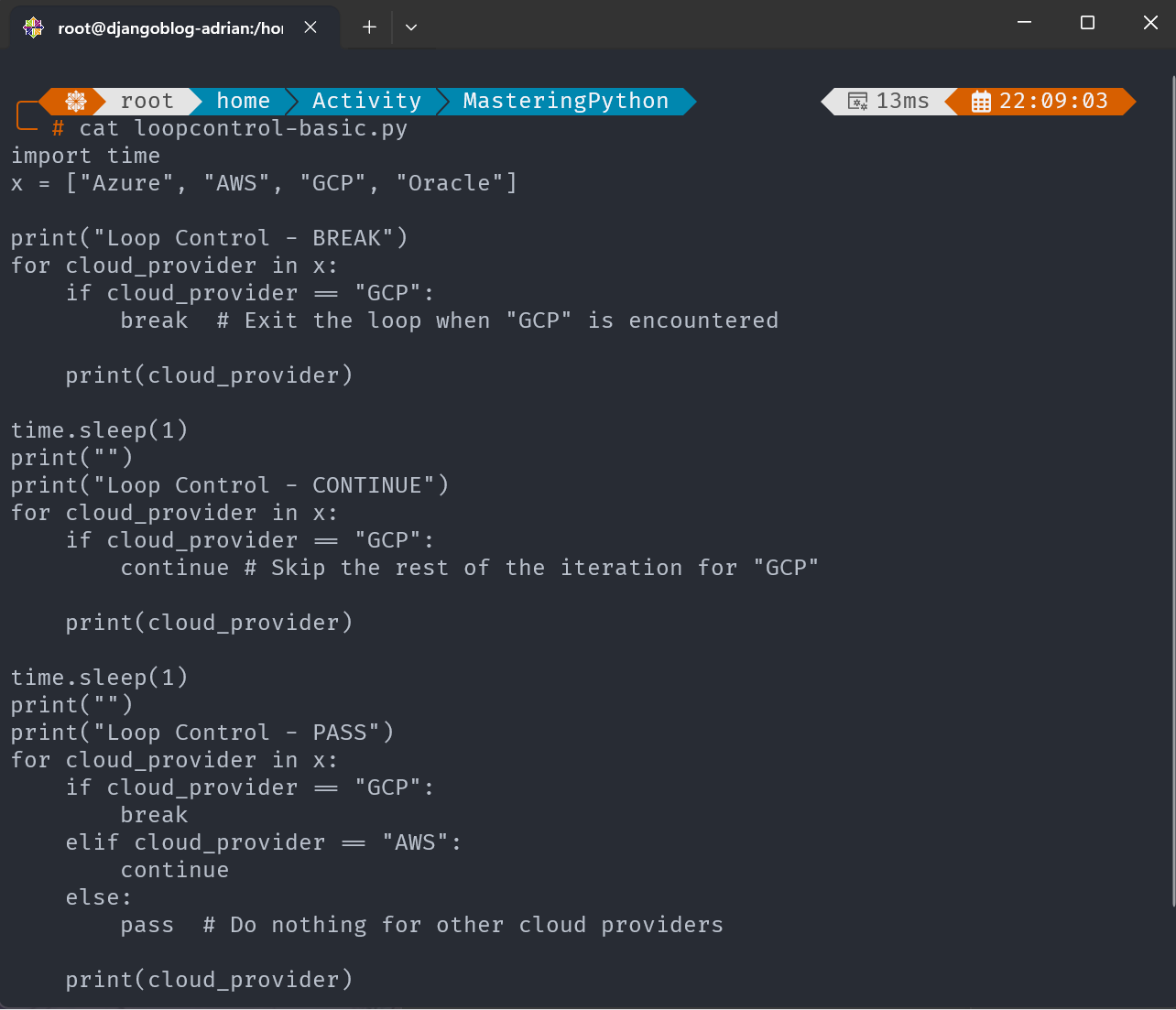
Conclusion
With Python's operators, conditional statements, and loops, you can handle any logic your script may require. Developing robust Python programs starts with these core structures.
Stay tuned for the next blog, where we’ll explore Python's Essential Libraries for DevOps to further expand your scripting toolkit!
Day 16: Mastering Python Control Flow and Core Structures
Learn Python's essential control structures, including operators, conditional statements, loops, and loop controls to master DevOps programming concepts.
For the passion of automated cloud solutions.
Subscribe to get the latest posts. I mostly write about Backend (Python/Bash), DevOps and Linux.