Day 2: Mastering The Linux Basic Commands Part 2
Aug 5, 2024
•01:18 AM GMT+8

As we continue mastering the basic Linux commands, this blog will cover System Information and Processes, Permissions and Ownership, and Basic Networking.
System Information and Processes
- top command
Displays real-time system processes and resource usage.
top
- ps command (Process Statuses)
Lists currently running processes. Useps aux | grep processfor specific process detailed view.
ps
ps aux
ps aux | grep python
- kill command
Terminates a process by its ID (PID). Usekill -9for a forceful termination.
kill PID
- df command (Disk Free)
Shows disk space usage. Usedf -hfor a human-readable format.
df
df -h
- free command
Displays memory usage, withfree -hproviding a human-readable format.
free
free -h
Permissions and Ownership
chmod command (Change Mode)
Modifies file or directory permissions. Here's how to read and understand these permissions as given in this example-rwxr-xr--This string is divided into four parts:
File Type Indicator (-ordorl):
The first character represents the type of file:-: Regular filed: Directoryl: Symbolic linkUser (Owner) Permissions (
rwx):
The next three characters represent the permissions for the user who owns the file:r: Read permission (4)w: Write permission (2)x: Execute permission (1)
Example:rwxmeans the user has read, write, and execute permissions.Group Permissions (
r-x):
The following three characters represent the permissions for the group that owns the file:r: Read permission (4)-: No write permission (0)x: Execute permission (1)
Example:r-xmeans the group has read and execute permissions, but no write permission.Other (World) Permissions (
r--):
The final three characters represent the permissions for all other users:r: Read permission (4)-: No write permission (0)-: No execute permission (0)
Example:r--means others have read-only permission.Here's a detailed table explaining the
chmodcommand and the permissions it sets for files and directories in Linux:
| Symbol | Numerical Value | Permission |
| --- | 0 | No Permission |
| --x | 1 | Execute |
| -w- | 2 | Write |
| -wx | 3 | Write & Execute |
| r-- | 4 | Read |
| r-x | 5 | Read & Execute |
| rw- | 6 | Read & Write |
| rwx | 7 | Full Permission |
# Chown Permissions
chmod 777 filename #Full Permissions for User, Group, and Others (777)
chmod 644 filename #Read and Write for User, Read Only for Group and Others (644)
chmod 750 filename #No Permissions for Others (750)
chmod u+x filename #Add execute permission for the user
chmod o+x filename #Remove write permission for others
chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r filename #Set read and write for user, and read for group and others
- chown command (Change Ownership)
Changes file or directory owner and group.
chown user:group directory/file
chown -R user:group directory/file #operate on files and directories recursively.
Networking
- ping command
Tests connectivity to a network host.
ping example.com
- ifconfig command
Displays network interface information.
ifconfig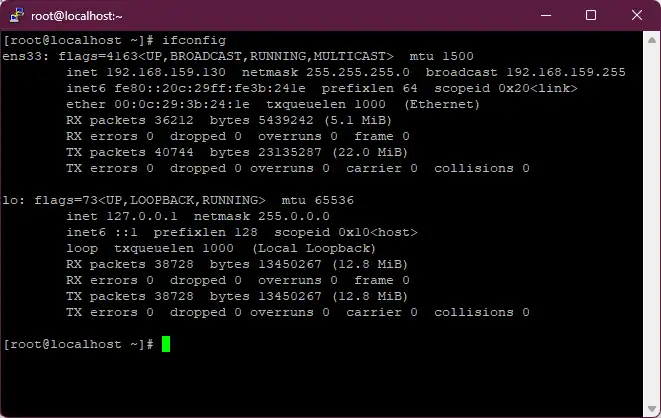
- curl command
Transfers data from or to a server using supported protocols (HTTP, FTP, etc.). More details on how to use curl are on this blog site curl-command-in-linux.
curl -I http://example.com #Fetch the HTTP-header only!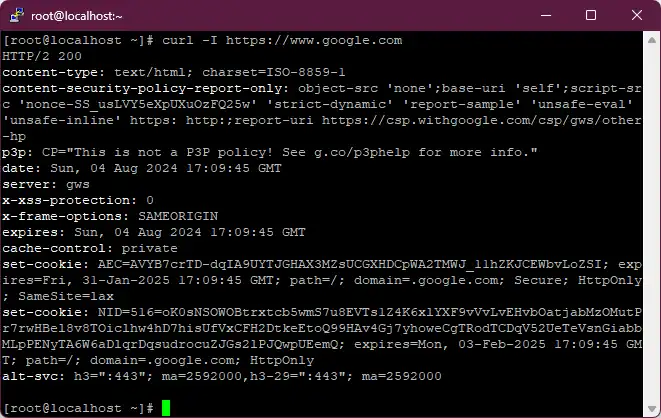
💡 Checking out this website explainshell is very helpful if you want to learn more about command-line usage, including arguments.
Wrap-up
This guide provides an overview of essential concepts and commands in the Linux system. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial in the world of DevOps. In the next blog, we will explore how the Linux environment can be utilized to automate processes through bash/shell scripting.
Day 2: Mastering The Linux Basic Commands Part 2
Build upon your Linux foundation as we investigate deeper into essential commands for System Information and Processes, Permissions and Ownership, and basic networking.
For the passion of automated cloud solutions.
Subscribe to get the latest posts. I mostly write about Backend (Python/Bash), DevOps and Linux.