Day 8: Mastering Software Management with Linux Package Managers and systemctl
Aug 25, 2024
•11:02 PM GMT+8

The 8th day of the challenge has begun! The Linux package manager and systemctl are two essential tools for managing software and system services on Linux. The use of these tools is crucial for efficient system administration and automation.
The Linux Package Manager
Installing, updating, and removing software is handled by package managers in Linux distributions. You might use a different package manager depending on your distribution. Here is a quick overview of the most common ones:
APT (Advanced Package Tool)
APT is commonly used on Debian-based systems such as Ubuntu and Debian. It supports commands like apt and apt-get for managing software packages.
YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified)
YUM is commonly used on RHEL-based systems, including CentOS and Fedora. It provides an easy way to manage software packages, including installing, updating, and removing them.
DNF (Dandified YUM)
DNF is the newer package manager used on more recent RHEL-based distributions like Fedora. It replaces YUM while offering similar functionality but with improved performance and better dependency management.
Tasks
Install Docker using your system's package manager.
Before installing the latest Docker engine for the first time, install the yum-utils package(which provides the yum-config-manager utility) and added to the list of repository.
# Install Docker repository
yum -y install yum-utils
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repoTo install Docker on RHEL or CentOS, use these commands
# Install Docker
yum -y install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin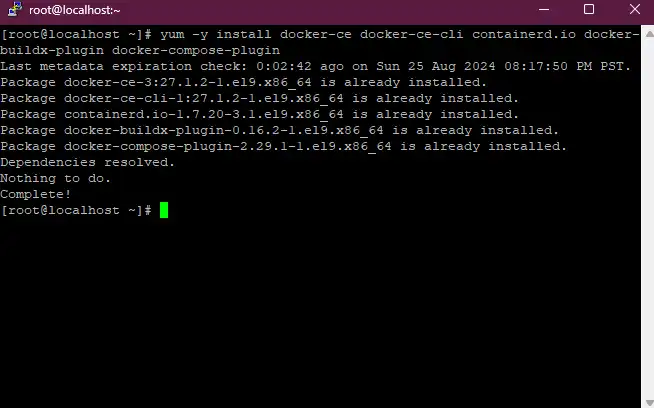
With this command, we can combine all necessary packages into one. As I have already installed Docker on my system, it's showing as already installed.
Once we installed the Docker, we can verify with this command docker --version
docker --version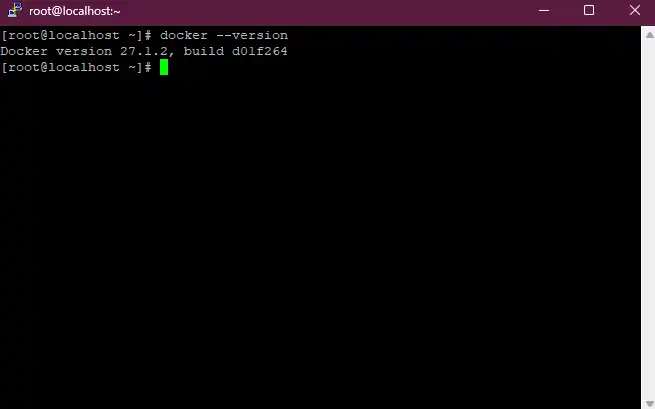
Managing System Services with systemctl
The systemctl is a command-line utility for managing services on a Linux system using systemd. It provides a straightforward way to control and monitor system services.
Basic Commands
- Start a Service:
sudo systemctl start service_name - Stop a Service:
sudo systemctl stop service_name - Restart a Service:
sudo systemctl restart service_name - Reload a Service Configuration:
sudo systemctl reload service_name - Check the Status of a Service:
systemctl status service_name - Enable a Service at Boot:
sudo systemctl enable service_name - Disable a Service at Boot:
sudo systemctl disable service_name
Combining Package Management and systemctl
Previously, we installed the Docker package. Now, we need to manage its service. To start and enable Docker, use this command:
# To start the docker service
systemctl start docker
# To check status of the docker service
systemctl status docker
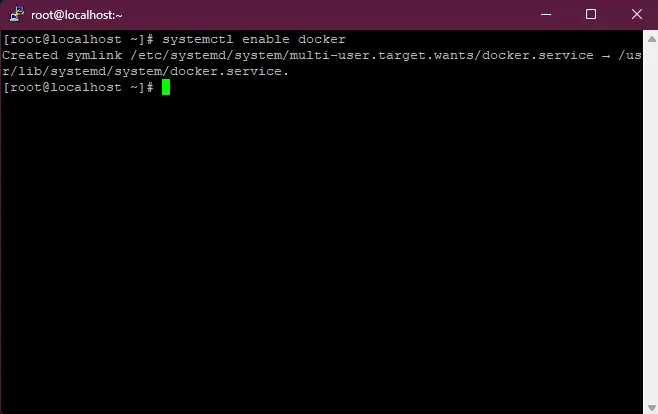
# To enable the docker service
systemctl enable docker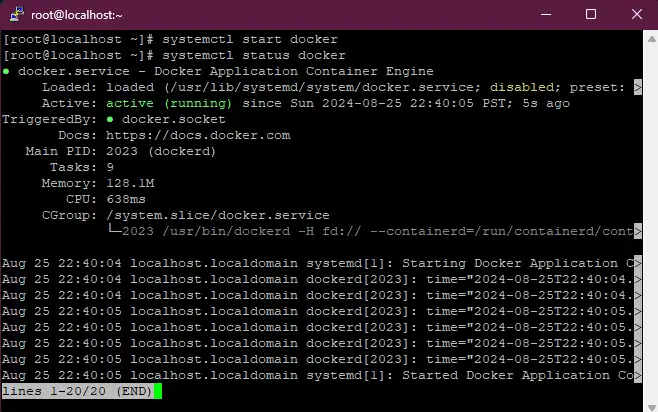
Conclusion
For effective software and system service management, you must understand how the Linux package manager works and how systemctl works. Using these tools, we can ensure that your Linux system runs smoothly and is well maintained.
As we move forward in this series, we will dive into Git, a powerful version control system that allows you to manage code changes and collaborate with others. Come back soon for an exploration of Git's features and best practices!
Day 8: Mastering Software Management with Linux Package Managers and systemctl
Explore essential tools for managing software and services on Linux with package managers and systemctl
For the passion of automated cloud solutions.
Subscribe to get the latest posts. I mostly write about Backend (Python/Bash), DevOps and Linux.